Fokussieren Sie sich auf Ihr Geschäft!
Wir kümmern uns um Ihre Compliance
- Lieferketten-Compliance (LkSG, CSDDD)
- Hinweisgeberschutztool (HinSchG, LkSG )
- KYB-Compliance
- Sanktionslistenprüfung


Die digitale Plattform Trustnet.Trade setzt einen neuen Qualitätsstandard in der Compliance zwischen Unternehmen. Speziell entwickelt für die Geschäftspartnerprüfung (KYB) und die Anforderungen an die Lieferketten-Compliance nach LkSG und CSDDD. Nachhaltig, zukunftsfähig für künftige regulatorische Anforderungen im ESG-Spektrum.
KYB Compliance
Mit einem Klick identifizieren Sie die Eigentümerstruktur und alle wirtschaftlich Berechtigten Ihres Geschäftspartners (UBO) und prüfen diese gegen Sanktionen, Embargos, AMS und PEP.
Lieferketten-Compliance
Führen Sie die Risikoanalyse automatisiert durch, bauen Schritt für Schritt ein Risikomanagement auf und sichern eine Revisionssichere Dokumentation.
Hinweisgeberschutztool
Erfassen Sie über das Hinweisgebertool von Trustnet.Trade eingehende Hinweise von eigenen Mitarbeitenden oder Mitarbeitenden bei Kunden und Lieferanten. Decken Sie Rechtsverstöße in Ihrer Wertschöpfungskette auf.
Trustnet.Trade
Ein Produkt der Cargodian GmbH
Warum Trustnet.Trade?
Hinweisgeberschutz
Risikoanalyse und Monitoring

Prüfungen vor Ort

Praktische Handlungs-empfehlungen

Trustnet.Trade Ecosystem


Trustnet.Trade

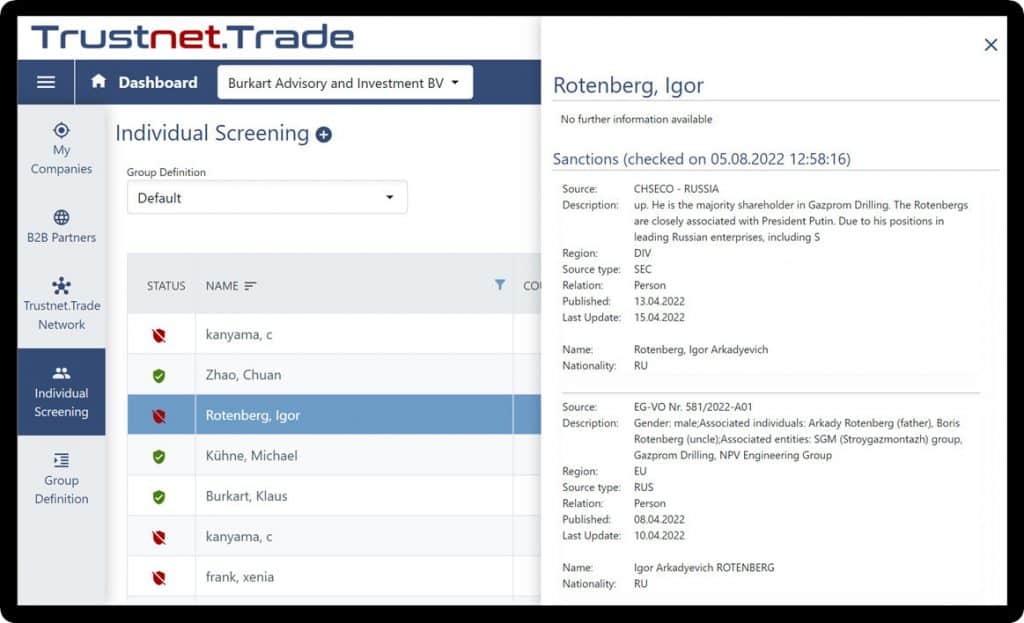
Trustnet.Trade führt eine umfassende Prüfung auf Sanktionen, Embargos, AMS, PEP für jedes identifizierte Unternehmen und jede Person (Ultimate Beneficial Owner, UBO) in der Eigentümerhierarchie Ihres Geschäftspartners durch.
Der KYB-Check entspricht den Vorschriften des deutschen, europäischen und des US-Geldwäschegesetzes.
Je nachdem, wie viele wirtschaftliche Eigentümer ermittelt wurden, dauert die Überprüfung zwischen 5 und 30 Sekunden.
Nach erfolgreicher Überprüfung kann ein Trustnet.Trade-Widget auf Ihre Website hochgeladen werden. Dieses Widget wird automatisch in Echtzeit aktualisiert. Es zeigt den Besuchern Ihrer Website deutlich Ihren proaktiven Ansatz und schafft Vertrauen.

Hinweise können über einen Link auf Ihrer Website personalisiert oder anonym angegeben werden. Eingehende Hinweise werden dann in der geschützten Umgebung von Trustnet.Trade bearbeitet und Ihre Mitarbeiter oder eine externe Stelle informiert.
Trustnet.Trade analysiert umfassend Datenquellen, um generische und spezifische Risiken für Länder und Geschäftspartner in einer Wertschöpfungskette zu erfassen. Risiken werden in einer Heatmap dargestellt. Durch Selbstauskünfte und Checks von lokalen Experten vor Ort können Risikoindikationen validiert werden.
Sollten durch die Risikoanalyse Risiken oder Verstöße identifiziert worden sein, werden im Risikomanagement angemessene Maßnahmen zugeordnet und verwaltet. Maßnahmen können kategorisiert und priorisiert, verantwortlichen Personen zugewiesen, Prüf- und Bearbeitungsaufträge erteilt und Termine überwacht werden.
Prüfungen werden durch unsere Partner Vor-Ort entweder über Desktop oder Live beim Lieferanten durchgeführt. Das Regelwerk dafür wird über Trustnet.Trade bereitgestellt.
Lieferketten- Compliance (LkSG, CSDDD), Risikoanalyse, Risikomanagement, Beschwerdemanagement. Benutzerfreundliche Anwendung. Echter Kundenservice (kein Chatbot).
Das Trustnet.Trade Widget

Je nachdem, welche Prüfungen Sie bereits durchlaufen haben, leuchten die einzelnen Punkte in der Legende grün auf. Weiterhin wird ein Gültigkeitsdatum ihres Widgets angezeigt und entsprechend verlängert, wenn die Prüfung erneut durchgeführt wurde.
Unsere Kunden und Partner






















Jetzt Promocode sichern!
Möchten Sie mehr über unsere Produkte oder Cargodian im Allgemeinen erfahren? Wir freuen uns über Ihre Nachricht.
Sichern Sie sich jetzt einen Promocode und testen Sie die Plattform!
 Zum Inhalt wechseln
Zum Inhalt wechseln
